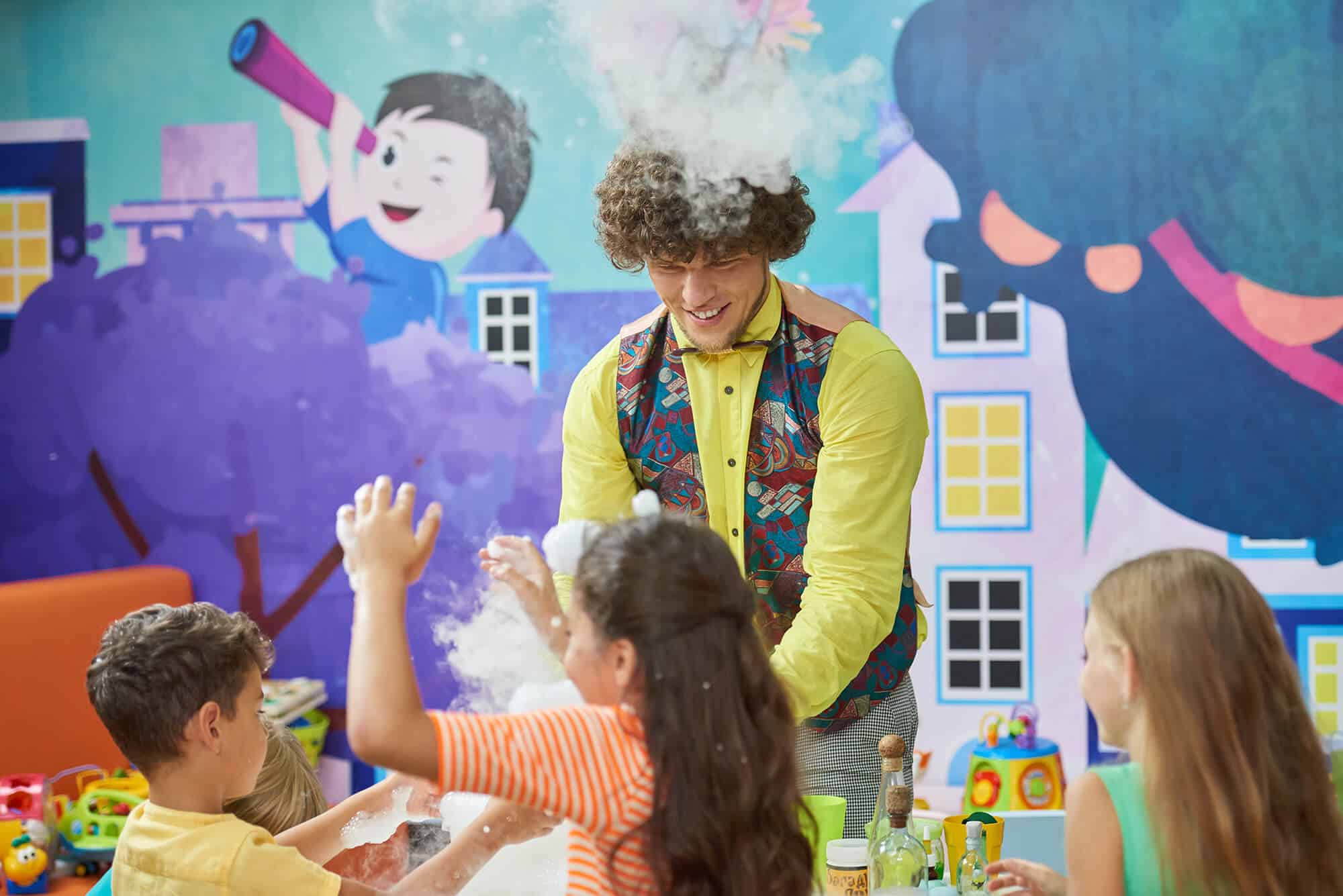Introduction
In today’s digital age, handwriting might seem like a fading art. However, for children, developing neat handwriting is crucial for academic success and self-expression. Clear handwriting enhances reading comprehension, boosts confidence, and fosters effective communication.
If your child struggles with messy handwriting, don’t worry. With the right techniques and a bit of patience, you can help them improve their penmanship.
Understanding the Importance of Handwriting
Handwriting is more than just putting pen to paper; it’s a complex skill that integrates cognitive development, fine motor skills, and visual perception. Research indicates that children with legible handwriting tend to perform better academically, as it aids in note-taking, test-taking, and overall communication.
Moreover, the act of writing by hand engages the brain differently than typing, promoting better memory retention and understanding.
Common Challenges in Children’s Handwriting
Children may face various obstacles when learning to write neatly:
- Poor Pencil Grip: Holding the pencil incorrectly can lead to hand fatigue and illegible writing.
- Weak Fine Motor Skills: Underdeveloped muscles in the hands and fingers can make controlling the pencil difficult.
- Lack of Practice: Infrequent writing can hinder the development of consistent handwriting habits.
- Learning Differences: Conditions like dysgraphia or ADHD can affect handwriting abilities.
Identifying these challenges early allows for targeted interventions to support your child’s writing development.
Effective Strategies to Improve Handwriting
1. Establish Proper Grip and Posture
- Tripod Grip: Teach your child to hold the pencil using the tripod grip—pinching the pencil between the thumb and index finger while resting it on the middle finger.
- Posture: Ensure your child sits upright with feet flat on the floor, back straight, and the non-writing hand holding the paper steady.
- Paper Position: Angle the paper slightly to match the natural movement of the writing hand.
2. Strengthen Fine Motor Skills
Enhance hand and finger strength through fun activities:
- Playdough Manipulation: Rolling, pinching, and shaping playdough can build muscle strength.
- Bead Stringing: Threading beads onto a string improves hand-eye coordination.
- Scissor Cutting: Cutting along lines helps develop control and precision.
- Drawing and Coloring: Encourage detailed coloring within lines to enhance control.
3. Implement Structured Practice Routines
- Daily Practice: Set aside 10-15 minutes each day for focused handwriting exercises.
- Use Lined Paper: Lined paper guides letter size and alignment.
- Positive Reinforcement: Praise efforts and improvements to build confidence.
4. Make Handwriting Practice Fun
Transform writing practice into enjoyable activities:
- Creative Writing Prompts: Encourage storytelling to make writing engaging.
- Writing Games: Play games like “write the missing letter” or “word scavenger hunts.”
- Art Integration: Combine drawing and writing by labeling pictures or creating comic strips.
5. Leverage Resources and Support
Utilize available tools and programs:
- Handwriting Improvement Club: Join our Handwriting Improvement Club for structured lessons and resources.
- Educational Apps: Incorporate apps designed to improve handwriting skills through interactive activities.
- Professional Guidance: Consult occupational therapists for personalized strategies if needed.
Conclusion
Improving handwriting is a journey that combines patience, practice, and encouragement. By implementing these strategies, you can support your child in developing neat and confident handwriting skills that will benefit them throughout their academic and personal lives.
Remember, every child progresses at their own pace. Celebrate small victories and maintain a positive attitude to foster a love for writing.
FAQs
Q1: At what age should children start handwriting practice?
Children can begin developing pre-writing skills around ages 3-4, with formal handwriting instruction typically starting at age 5-6.
Q2: How long should daily handwriting practice sessions be?
Short, consistent sessions of 10-15 minutes are effective, ensuring children remain engaged without feeling overwhelmed.
Q3: What tools can aid in improving handwriting?
Tools like pencil grips, lined paper, and ergonomic pens can assist children in developing proper writing techniques.